Dementia is a progressive neurological disorder that affects memory, cognitive abilities, and behaviour, significantly reducing an individual’s ability to perform daily activities independently. It is a growing concern for older adults globally, with the number of affected individuals expected to rise significantly in the coming years. Identifying effective interventions to address cognitive and emotional challenges associated with dementia is crucial to the well-being of affected individuals and their caregivers.
Highlights
- Music therapy is a promising non-pharmacological intervention for dementia patients, helping improve cognitive and emotional functions.
- Improved language functioning, social engagement, and reduced agitation are potential benefits of music therapy for people with dementia.
- Continued research on the effectiveness of music therapy in dementia care will help refine and expand its practical applications.
Music therapy has emerged as a promising non-pharmacological intervention for people with dementia. It involves the use of musical elements such as rhythm, melody, and harmony to facilitate communication, expression, and interaction.Researchers at the University of Toronto and Unity Health Toronto suggest that this therapeutic modality may have a positive influence on the cognitive, emotional, and behavioural aspects of dementia patients, whilst offering a pleasant and engaging experience.
The potential benefits of music therapy for dementia patients are vast, including improved language functioning, increased social engagement, and reduction in agitation or aggressive behaviours. With an ever-growing body of research, it is crucial to further examine the effectiveness of music therapy in this population and explore how it can be integrated into dementia care practices as a valuable therapeutic tool.

What Is Music Therapy
Music therapy is a delightful and effective way to enhance well-being, particularly for those facing health challenges. It’s a therapeutic practice that involves using music to address physical, emotional, cognitive, and social needs of individuals.
In its simplest form, music therapy might involve listening to calming tunes to ease stress, or it could be as engaging as participating in a group sing-along to boost social interaction. It’s not just about listening, though; it can also include creating music, singing, moving to music, or playing instruments.
The beauty of music therapy is that it can be tailored to each person’s preferences and needs. It can help improve mood, reduce anxiety, enhance concentration, and even improve motor skills and coordination. It’s a charming and often joyful way to support healing and emotional well-being, making it a wonderful tool in the care of individuals with a variety of conditions.
Music Therapy’s Role In Dementia
Music therapy has increasingly become a popular intervention for individuals suffering from dementia. In this section, we will explore the benefits of music in therapy and its impact on behavioural and psychological symptoms.

Benefits of Music in Therapy
Music therapy involves the use of musical elements such as singing, dancing, playing musical instruments, and music listening to achieve therapeutic goals. The power of familiar music, in particular, can bring back memories and stir emotions, leading to:
- Improved mood and reduced depression
- Enhanced social interaction and communication
- Increased overall engagement and cognitive stimulation
Moreover, individuals with dementia have been observed to respond better in music-based intervention settings, even as their cognitive functions continue to decline.
Impact On Behavioural And Psychological Symptoms
Behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) are commonly associated with dementia and can negatively affect a person’s quality of life – such as agitation and aggression, depression, anxiety, hallucinations and delusions, apathy, sleep disturbances, wandering, and eating and feeding difficulties. Music therapy has demonstrated positive effects in mitigating these symptoms:
- Reduction in agitation: Familiar music has been observed to reduce agitation and restlessness in individuals with dementia.
- Enhanced communication: Singing and playing musical instruments may support non-verbal communication skills, helping patients express themselves more effectively.
- Social connection: Engaging in group music therapy sessions provides an opportunity for individuals to interact socially with others, potentially reducing feelings of isolation.
- Stress management: Music listening, as a form of relaxation, can help alleviate anxiety and stress.
Music therapy can play a crucial role in improving the well-being of individuals with dementia. By harnessing the power of music, this therapeutic approach promotes enhanced quality of life and fosters positive behavioral and psychological outcomes in dementia patients.
Effects Of Music Therapy On Cognitive Functions
Music therapy has gradually emerged as a potential intervention to support cognitive functions in patients with dementia. This alternative and non-pharmacological approach has been the subject of numerous systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and clinical trials to assess its effectiveness on cognitive functions, such as memory, orientation, and executive functions.

Enhancing Memory
One key aspect of cognitive functions that music therapy may have a positive influence on is memory. Recent studies suggest that music therapy may have the potential to alleviate some progressive memory loss often associated with dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. It seems that music-based therapeutic interventions can effectively stimulate brain plasticity and lead to the formation of new neural connections, thus enhancing musical memories and overall cognition.
Music therapy’s effect on memory is not just limited to musical memories. Some studies accredited it as an aid that helps patients recall information, events, and other non-musical memories, leading to improvements in cognitive outcomes, in addition to orientation and recognition.
Impacts on Executive Function
Executive functions refer to a group of higher-order cognitive processes that govern goal-directed behaviors. Music therapy has been found to have modest but positive impacts on executive functions in patients with dementia. Some clinical trials have reported that this therapy may improve general cognition, as well as specific skills, such as planning, organizing, and problem-solving. Deficits in these functions are typical symptoms of dementia, and music therapy interventions might help ameliorate the impacts of these conditions on affected individuals.
While the magnitude of music therapy’s effects on executive functions may be considered slight, some neurologists still recognize its potential in positively affecting cognitive outcomes in patients with dementia. These interventions can contribute to the formation of new neurons and neural pathways, enhancing brain plasticity and potentially improving executive function capabilities.
Influence on Verbal Fluency
Another area where music therapy may have some positive effect is on verbal fluency, an essential component of language functioning. Studies have assessed the impact of music therapy on verbal fluency in patients with dementia and found that this intervention might lead to notable improvements in patients’ ability to produce meaningful speech, articulate their thoughts, and engage in conversation.
These benefits could be attributed to music therapy’s capacity to stimulate different regions of the brain involved in language processing. Patients with dementia who undergo music therapy interventions may experience enhanced cognitive function, including improved verbal fluency, as their brain adapts and forms new connections.
Overall, music therapy shows promising results in addressing cognitive functions in patients with dementia. It’s important to continue with further research and clinical trials to fully understand the potential of these interventions, as they may become a valuable way to support and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by this debilitating condition.
Music Therapy’s Influence On Emotional State
Music therapy has emerged as a beneficial intervention for individuals with dementia, targeting various aspects of their emotional well-being. This section will delve into the specific benefits of music therapy, namely combating depression, reducing anxiety, and boosting mood.
Combating Depression
Depression is a common symptom associated with dementia, and studies have found music therapy to be an effective approach in addressing this issue. Meta-analyses reveal that music therapy can significantly improve the depressive state in patients with dementia. Through engagement in musical activities, individuals can experience emotional rewards, leading to a reduction in feelings of depression. Moreover, music therapy can enhance verbal communication and social interactions, helping to ease feelings of isolation often experienced by those with dementia.
Reducing Anxiety
Anxiety is another emotional challenge faced by individuals with dementia. Music therapy has been shown to alleviate trait anxiety in patients by eliciting positive emotions and promoting relaxation. By participating in music therapy sessions, patients can develop a greater sense of control over their emotions and derive comfort from the familiar auditory environment. This therapeutic approach provides an opportunity for emotional expression and regulation, ultimately leading to a reduction in anxiety levels.
Boosting Mood
Music therapy has a powerful impact on the overall mood of individuals with dementia. Integrating musical elements can evoke memories and emotions tied to personal experiences, resulting in an improved emotional state. Alzheimer’s disease, in particular, can often cause apathy and emotional detachment; however, music therapy can help reconnect patients with their emotions and foster a sense of emotional reward.Through active music-making or simply listening to meaningful tunes, patients can experience mood uplifts and enhanced quality of life.
Overall, music therapy offers a range of benefits for individuals with dementia, addressing critical emotional challenges such as depression, anxiety, and overall mood. By engaging in musical activities, patients can build connections with their emotions and memories, resulting in a more rewarding and fulfilling experience throughout the course of their dementia journey.
Taking Part In Music Therapy
Active Versus Passive Participation
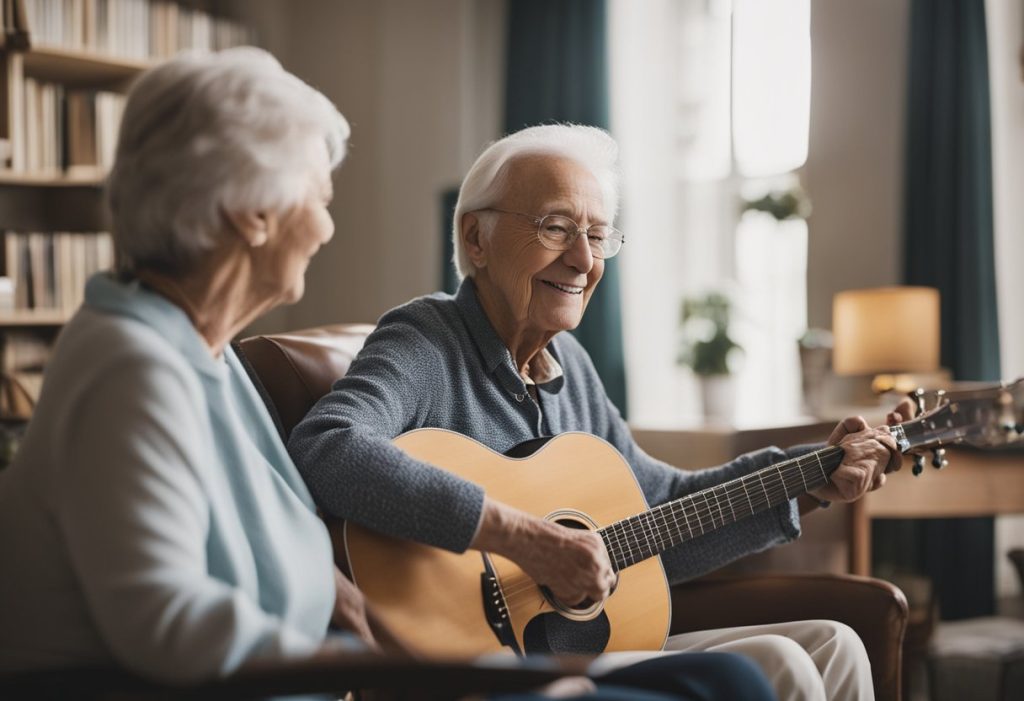
Music therapy offers various ways for individuals with dementia to engage and benefit from the therapeutic experience. Active participation involves the person directly taking part in the music-making process, such as playing an instrument, singing, or moving to music. This active involvement fosters communication, engagement, and contributes to enhancing their quality of life.
On the other hand, passive participation involves the person simply listening to music or engaging in music and relaxation exercises. This approach also has its benefits, as it allows people with dementia to tap into their musical memory, evoking emotions and soothing anxiety.
Use of Familiar Versus New Music
The choice of music in a therapy session plays an essential role in determining its effectiveness. Familiar music, particularly from the individual’s past, may evoke positive memories and emotions. This can stimulate conversation and emotional bonding, helping the person to connect with memories and experiences that may have otherwise been difficult to access.
Benefits of Familiar Music | Benefits of New Music |
|---|---|
| Evoking emotions | Encouraging curiosity |
| Stimulating conversation | Promoting exploration |
| Emotional bonding | Enhancing creativity |
In contrast, using new and less familiar music in therapy sessions can encourage curiosity, exploration, and creativity. While both familiar and new music can effectively engage people with dementia, the choice will largely depend on the individual’s preferences and needs.
Music therapy can be adapted to suit the particular requirements and preferences of individuals with dementia. By taking into account active and passive participation, as well as selecting the most appropriate types of music, therapists can provide tailored and effective interventions to improve the quality of life for those living with dementia.
Comparative Analysis: Pharmacological Versus Non-Pharmacological Interventions
A variety of interventions exist for the treatment of dementia, including pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches. Systematic reviews of these interventions have shown mixed results. Pharmacological treatments, such as cholinesterase inhibitors and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, can slow cognitive decline and alleviate dementia symptoms. However, they also come with a risk of side effects.
On the other hand, non-pharmacological interventions like music therapy have been studied in randomized controlled trials. Some trials suggest that music therapy may not have a significant effect on agitation, while others indicate that it could be effective in improving mood, reducing anxiety and alleviating behavioural symptoms.
Important findings from clinical trials include:
- Cholinesterase inhibitors and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors can slow cognitive decline and improve dementia symptoms in some patients
- Music therapy may improve patients’ mood, reduce anxiety and alleviate behavioural symptoms, though results are not consistent across all trials
Choosing the Right Treatment
When it comes to selecting the most appropriate treatment option for people with dementia, consider factors such as the severity of the condition, the patient’s preferences, and the potential risks and benefits of each intervention.
In cases where dementia symptoms are mild, non-pharmacological interventions like music therapy could be worth exploring. Such interventions can be seen as a more gentle alternative to medications and can potentially help improve patients’ quality of life.
As the dementia progresses and symptoms become more debilitating, pharmacological interventions might be necessary. Medications such as cholinesterase inhibitors can help manage cognitive and functional decline, but caution should be taken to monitor side effects.
Both pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions have proven beneficial in treating dementia symptoms. A comprehensive treatment plan should take into account each patient’s unique situation and requirements, often incorporating a combination of therapies to provide optimal care and support.
Dementia Music Therapy
Music therapy has been increasingly recognized as a beneficial intervention for individuals with dementia. Engaging in music therapy can induce relaxation, potentially reducing stress levels in both the aging population and their caregivers. While listening to music, dopamine is released which can help improve motor function and enhance overall well-being.
Research has shown that music therapy can have a positive impact on cognitive and non-cognitive outcomes in elderly dementia patients. Various case studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of this therapy in slowing down the progression of neurodegeneration, which is a significant concern in dementia.
Incorporating music therapy into the daily lives of individuals with dementia may offer additional benefits to their immune system. Studies suggest that reducing stress levels can have a positive effect on the immune response, thereby supporting the body’s ability to combat various illnesses and diseases.
While it is important to recognize the promising benefits of music therapy in dementia care, it should be noted that more research is needed to develop standardized protocols and determine the most effective strategies for implementation. Additionally, it is crucial to prioritize the well-being of the individuals participating in these therapies, ensuring they are comfortable and receptive to the intervention.
In conclusion, music therapy provides a valuable option for enhancing the quality of life for individuals with dementia. Offering a non-pharmacological intervention, it holds potential for improving cognitive function, reducing stress, and promoting overall well-being in an aging population. Practitioners and families may consider incorporating music therapy into their care plans as a complementary approach to traditional dementia treatments.